Recent research out of the University of Gothenberg indicates that increasing surface roughness of implants at the nano level speeds the integration process.
Increasing the Active Surface of Dental Implants at Nano Level Quickens Healing
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have conducted studies on the surface arrangement of dental implants both at the micro and nano level to enable speedy healing of patients.
Johanna Löberg from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gothenburg stated that by causing an increase of the active surface area at the nano scale and altering the implant’s conductivity, the biomechanics of the body is influenced in such a way as to avoid discomfort and to speed up the healing process.
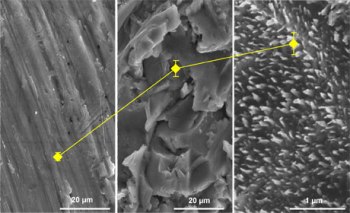
It was evident that the surface of dental implants is often associated with the level of roughness, from the superimposed nanostructures to the thread. When the implant is placed in the bone, the bone tissue experiences a mechanical force known as biomechanical stimulation, which leads to the formation of new bone. Although roughness is not the only factor that influences healing, it is crucial for new bone formation. It is also necessary to measure and illustrate the appearance of the surface in detail.
Johanna Löberg has formulated an approach that explains the topography of the implant from nanometre to micrometre scale. This approach enables theoretical estimation of placing the implant in the bone by diverse surface topographies. It can be used to develop new dental implants and to enable optimization of properties for quick healing and increased bone formation. The results demonstrate that a small increase in conductivity delivers improved cell response and quick deposition of minerals that are essential for bone formation. Surfaces with a clearly defined nanostructure feature a larger active area and react faster to the deposition of bone-forming minerals.
The project was performed by the University of Gothenburg in collaboration with the Astra Tech AB in Mölndal, and has scope for further study.
Source: http://www.science.gu.se/